Inquiry
LiFePO4 vs AGM Marine Batteries: Which Powers Your Boat Best?
Choosing a battery for your boat isn’t just about volts and amps—it's about trust, cost, safety, and performance. For years, AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries have been a go-to for marine users. But more recently, LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries have entered the scene with big promises: longer life, faster charging, and better performance.
So, in the face-off between LiFePO4 vs AGM batteries for marine applications, which truly fits your needs? The answer isn’t one-size-fits-all. LiFePO4 vs AGM marine batteries—each has strengths and trade-offs. Whether you’re fishing on a quiet lake, sailing off-grid, or running a commercial ferry, this guide compares performance, cost, safety, and more to help you decide. From lightweight power to budget-friendly reliability, here’s what you need to know.
What Are AGM and LiFePO4 Batteries?
Before diving into the comparison, let’s break down the basics of these marine battery types.
AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) Batteries
AGM batteries are sealed lead-acid batteries. Their absorbent fiberglass mats hold the acid, making them spill-proof and low-maintenance. They’re sealed, vibration-resistant, and widely used in marine applications for their reliability. They’ve long been used in boats for starting engines, powering lights, and supporting electronics.
AGM Battery Advantages:
- Lower upfront cost ($100-200 for 100Ah)
- Compatible with existing chargers and wiring
- Proven reliability for occasional or low-cycle use
- Better cold-weather cranking performance
AGM Battery Limitations:
- Short lifespan (300–500 cycles)
- Heavy and bulky (60–70 lbs for 100Ah)
- Slower charging (6-12 hours)
- Lower usable capacity (~50%)
- Loses performance if not fully charged regularly
LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) Batteries
LiFePO4 is a newer lithium-ion chemistry with strong safety and stability features. It's becoming increasingly popular for off-grid, solar-powered, and electric marine applications.
LiFePO4 Battery Advantages:
- Long lifespan (3000–5000+ cycles)
- Lightweight (25–30 lbs for 100Ah)
- Fast charging and higher energy efficiency
- Flat voltage curve: consistent power throughout discharge
- Smart BMS control for protection and monitoring
- zero maintenance, stable voltage
LiFePO4 Battery Limitations:
- Higher upfront cost ($300–700 for 100Ah)
- Requires a lithium-compatible charger and BMS
- Retrofitting may require wiring or system upgrades
- Charging below 0°C requires low-temperature protection
Head-to-Head Comparison: LiFePO4 vs AGM
Let’s compare the two across key metrics critical for marine use.
| Feature | LiFePO4 | AGM |
|---|---|---|
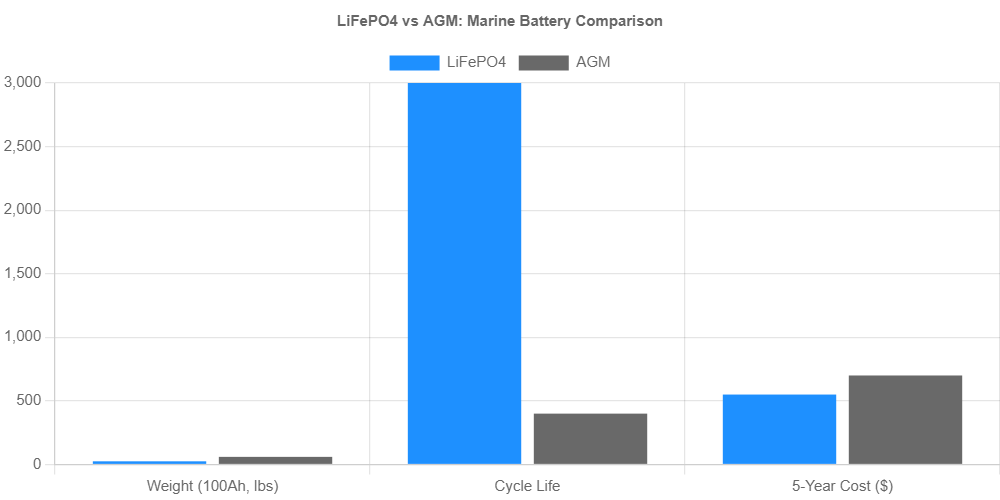
| Cycle Life | 3000–5000+ | 300–500 |
| Weight (100Ah) | 25–30 lbs | 60–70 lbs |
| Depth of Discharge | 80–100% usable | 50–60% recommended |
| Charging Speed | 1–2 hours(with proper charger) | 6–12 hours |
| Voltage Stability | Flat at 12.8V | Drops as charge declines |
| Maintenance | None | Occasional charge/top-up |
| Durability | IP67-sealed, saltwater-ready | Needs dry mounting, cover |
| Cold Performance | Needs BMS temp control | Naturally cold-tolerant |
| Initial Cost | $300–600 | $100–200 |
| 5-Year Cost | $550–700 | $600–700 |
Safety and Environmental Impact
Marine environments demand safe and eco-friendly batteries to protect your crew and the ocean.
- Safety: LiFePO4 batteries use stable chemistry, preventing thermal runaway and requiring no ventilation. AGM batteries risk acid leaks or hydrogen gas buildup but are safe with proper ventilation and maintenance.
- Environmental Impact: LiFePO4 is lead- and cadmium-free, recyclable through lithium programs. AGM’s lead content requires careful disposal via established recycling centers to avoid marine pollution.
- Certifications: LiFePO4 meets UL, CE, and UN38.3 standards; AGM complies with basic marine safety standards.
For example, a LiFePO4 battery’s IP67 casing resists saltwater corrosion, while AGM needs protective covers but has a proven safety record in controlled setups.
Takeaway: Both are safe with proper use, but LiFePO4’s green design aligns with modern marine regulations.
Customization and Compatibility
Every boat is unique, and battery choice depends on how well it fits your vessel’s systems.
- Customization: LiFePO4 batteries can be tailored for capacity (50-1000Ah), size, and features like Bluetooth BMS or low-temperature protection. AGM batteries are limited to standard sizes but widely available.
- Compatibility: LiFePO4 requires a compatible charger (14.4-14.6V) and sometimes wiring upgrades. AGM integrates seamlessly with existing lead-acid systems.
- Support: LiFePO4 suppliers offer ODM services for custom designs; AGM relies on universal models.
Example: A custom 200Ah LiFePO4 battery fits a yacht’s tight compartment and syncs with its solar system, while AGM’s standard sizes suit a fishing boat’s basic setup.
Need a tailored solution? Explore custom marine LiFePO4 battery options for your vessel.
Installation and Retrofitting
Upgrading your marine battery involves practical considerations.
- AGM: Plug-and-play with existing wiring and chargers, ideal for quick replacements. No special equipment needed.
- LiFePO4: May require a $100-200 charger upgrade and wiring adjustments for older systems. Custom solutions often include adapters and installation support.
Example: Swapping an AGM battery takes minutes, while a LiFePO4 retrofit for a sailboat might need a new charger but offers long-term efficiency.
Takeaway: AGM is simpler to install; LiFePO4’s custom kits ease complex upgrades.
When to Use LiFePO4 vs AGM Batteries on Your Boat
Fishing Boats & Trolling Motors
Scenario: Long hours running a trolling motor and fish finder.
- AGM: Provides 4-6 hours of runtime at 50-70A, affordable but heavy, requiring frequent recharges.
- LiFePO4: Delivers 8-12 hours at 100A, lightweight (25 lbs), and recharges in 1-2 hours.
Winner: LiFePO4 for performance and portability, but AGM works for shorter trips on a budget.
Sailboats with Solar & House Loads
Scenario: Powering lights, fridge, and navigation off-grid with solar.
- AGM: 80-85% charging efficiency, degrades with partial charges, lasts 3-5 years.
- LiFePO4: 95-98% efficiency, handles partial charges, lasts 10+ years with solar controllers.
Winner: LiFePO4 for off-grid reliability, though AGM suits small solar setups.
Explore solar-compatible LiFePO4 batteries with ACE Battery.
Engine Starting or Backup Power
Scenario: Starting engines or backing up electronics.
- AGM: High cold-cranking amps, reliable in cold weather, no special setup needed.
- LiFePO4: Needs high-peak discharge models and low-temp BMS for cold climates.
Winner: AGM for simplicity and cold-weather cranking, but LiFePO4 is viable with proper specs.
Commercial & Electric Boats
Scenario: Powering ferries, tour boats, or electric vessels with heavy loads.
- AGM: Limited by low capacity and frequent replacements for high-demand use.
- LiFePO4: High discharge (e.g., 600A), CAN bus integration, 20-30% fuel savings in hybrids.
Winner: LiFePO4 for durability and efficiency in demanding operations.
Cost Comparison: Is LiFePO4 Worth It?
Let’s break down costs for a 100Ah battery over 10 years.
| Factor | AGM | LiFePO4 |
|---|---|---|
| Battery Cost | $180 | $550 |
| Replacements Needed | 3–4 | 0–1 |
| Charging Efficiency | ~85% | ~95–98% |
| Cycle Count | 400 avg | 3000–5000+ |
| Estimated Total Cost | $600–700 | $550–600 |
Result: AGM’s low upfront cost suits casual boaters, but LiFePO4 saves money over time for frequent users.
Real-World Case Studies
- Fishing Boat (Florida): Swapped AGM for a 100Ah LiFePO4. Result: 10-hour runtime, 30% weight reduction, doubled trips.
- Weekend Cruiser (Maine): Used 100Ah AGM for lights and GPS. Result: Reliable power for 3 years at low cost.
- Solar Yacht (Mediterranean): Installed 400Ah LiFePO4 with Bluetooth BMS. Result: 7 days off-grid, real-time monitoring.
- Small Boat (Michigan): AGM powered basic electronics for occasional use, no maintenance issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I replace AGM with LiFePO4 directly?
Yes, but you’ll need a lithium-compatible charger (14.4-14.6V) and possibly wiring upgrades. Custom solutions often include adapters.
Are LiFePO4 batteries safe on boats?
Yes, LiFePO4’s stable chemistry prevents thermal runaway and off-gassing. AGM is safe with ventilation but risks leaks if damaged.
Can LiFePO4 handle cold climates?
Yes, with a BMS featuring low-temperature cut-off or heating. AGM performs well in cold without special features.
What’s the warranty on LiFePO4 vs. AGM?
LiFePO4: 5-10 years; AGM: 1-3 years, reflecting their lifespan differences.
How do I dispose of marine batteries?
LiFePO4: Recycle via lithium programs. AGM: Use lead-acid recycling centers to avoid pollution.
Is LiFePO4 worth it for occasional boaters?
AGM’s lower cost suits weekend use; LiFePO4 shines for frequent or off-grid sailors.
Choosing the Right Battery for Your Boat
- Choose AGM if: You’re a casual boater, need cold-weather cranking, or want a budget-friendly option.
- Choose LiFePO4 if: You sail frequently, use solar power, or need lightweight, long-lasting performance.
Tip: Custom LiFePO4 batteries can be tailored to your boat’s layout, power needs, or smart systems. Learn more about marine battery options with ACE Battery.
Conclusion: LiFePO4 or AGM?
LiFePO4 and AGM batteries each have a place in marine power. LiFePO4 excels for frequent sailors, off-grid adventurers, or high-performance boats with its long life, light weight, and efficiency. AGM remains reliable and affordable for casual boaters or simple setups. Evaluate your vessel’s needs—runtime, budget, and maintenance—to make the best choice.
Need help choosing? Contact us to explore LiFePO4 or AGM solutions for your boat.
Our expert will reach you out if you have any questions!